These deductions reduce a taxpayer’s taxable income for a given year or defer income taxes into future years. Tax shields lower the overall amount of taxes owed by an individual taxpayer or a business. A depreciation tax shield is a tax reduction technique under which depreciation expense is subtracted from taxable income. The amount by which depreciation shields the taxpayer from income taxes is the applicable tax rate, multiplied by the amount of depreciation. This tax shield can cause a substantial reduction in the amount of taxable income, so many organizations prefer to use accelerated depreciation to accelerate its effect.
Calculation Formula
We note from above that the Tax Shield has a direct impact on the profits as net income will come down if depreciation expense is increasing, resulting in less tax burden. In this context, it is important to understand what depreciation is. It is the method companies use to allocate the cost of an asset, which may be machinery, building, etc., throughout its useful life.
Depreciation Tax Shield Formula
Conversely, a services business may have few (if any) fixed assets, and so will not have a material amount of depreciation to employ as a tax shield. A person buys a house with a mortgage and pays interest on that mortgage. That interest is tax deductible, which is offset against the person’s taxable income. The concept of depreciation reflects the diminishing value of assets over time. The Depreciation Tax Shield accounts for this reduction by allowing businesses to deduct depreciation from taxable income, thereby reducing the overall tax burden. Taxes are a big part of expense optimization and cost-cutting strategies.
LTM Revenue (and EBITDA) in 3 Steps – The Ultimate Guide (
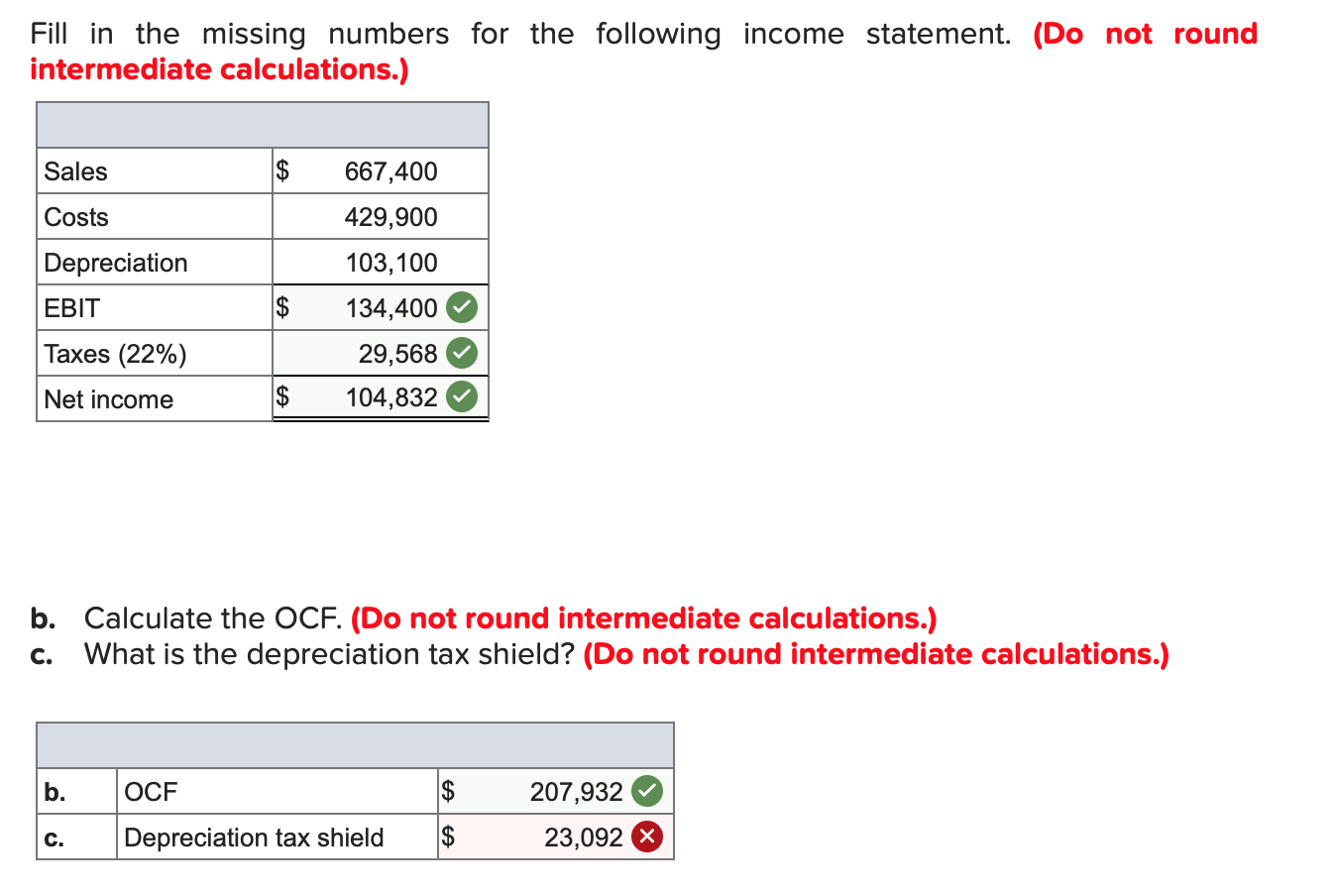
In Case we don’t take the Depreciation into account, then the Total Tax to be paid by the company is 1381 Dollar.
Tax Shield: Definition, Formula & Examples
Under U.S. GAAP, depreciation reduces the book value of a company’s property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) over its estimated useful life. Finally, we conclude on account of the above-stated cases that a tax shield can be utilized as a valuable option for effectively evaluating cash flow, financing, etc., activities. By comparing the above two options calculated, we concluded that the present value in the case of buying by taking a tax shield is lower than the lease option. A 25 % depreciation for plant and machinery is available on accelerated depreciation basis as Income tax exemption. Assume that the corporate tax is paid one year in arrear of the periods to which it relates, and the first year’s depreciation allowance would be claimed against the profits of year 1.
- If you deliberately claim specific tax credits that you’re not eligible for, then you are committing tax fraud.
- Let us consider an example of a company XYZ Ltd, which is in the business of manufacturing synthetic rubber.
- The concept is significant while making financial decisions in any capital-intensive business.
- With the two methods clarified, let’s look at the Cash Flow impact of each approach.
- Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
A tax shield on depreciation is the proper management of assets for saving the tax. A depreciation tax shield is a tax reduction technique under which depreciation expenses are subtracted from taxable income. The tax shield is a very important aspect of corporate accounting since it is the amount a company can save on income tax payments by using various deductible expenses. The higher the savings from the tax shield, the higher the company’s cash profit.
In addition, governments often create tax shields to encourage certain behavior or investment in certain industries or programs. Tax shields allow taxpayers to reduce the amount of taxes owed by lowering their taxable income. When flat bonus pay calculator filing your taxes, ensure you are taking these deductions so that you can save money when tax season arrives. Tax shields allow for taxpayers to make deductions to their taxable income, which reduces their taxable income.
The Debt used in the purchase creates Interest Expense that reduces the acquired Company’s Tax bill. In the section below, we cover two of the most common methods and their Cash Flow and Valuation impacts. There are a variety of deductions that can shield a company (or Individual) from paying Taxes. Therefore, the 1st option is better since it offers a lower cost of acquisition. This article is not intended to provide tax, legal, or investment advice, and BooksTime does not provide any services in these areas.
For example, because interest payments on certain debts are a tax-deductible expense, taking on qualifying debts can act as tax shields. Tax-efficient investment strategies are cornerstones of investing for high net-worth individuals and corporations, whose annual tax bills can be very high. The benefit of using depreciation with a tax shield is that you can subtract any depreciation expenses from taxable income. These intangible assets can affect your rate of tax and tax expense. It also has an option to write off only a minimum amount of $2,700.
Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. Tax evasion occurs when people intentionally fail to report their revenue or income to the proper taxing authority, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
The payment of the interest expense is going to ultimately lower the taxable income and the total amount of taxes that are actually due. Depreciation expense is an accrual accounting concept meant to “match” the timing of the fixed assets purchase—i.e. Capital expenditure (Capex)—with the cash flow generated from fixed asset over a period of time. The term “tax shield” references a particular deduction’s ability to shield portions of the taxpayer’s income from taxation. Tax shields vary from country to country, and their benefits depend on the taxpayer’s overall tax rate and cash flows for the given tax year. Let us take the example of another company, PQR Ltd., which is planning to purchase equipment worth $30,000 payable in 3 equal yearly installments, and the interest is chargeable at 10%.
